Ransomware is malicious software that denies you access to your computer or files until you pay a ransom.
There are several types of ransomware that are commonly seen:
- files/folders encryptors
- screen ‘lockers‘
- MBR ransomware (MBR: master boot record)
Files/folders encryptor
- it encrypts the contents of your My Documents folder – documents, spreadsheets, pictures, videos).
- Files are deleted once they are encrypted and there is a text file in the same folder with instructions for payment.
- You may see a lock screen but not all variants show one.
- Instead you may only notice a problem when you attempt to open your files. F
- r example, CryptoLocker is a file encryptor.



Screen Locker
–This version presents a full screen image that blocks all other windows and demands payment. No personal files are encrypted.
–Example: WinLocker

MBR ransomware
- MBR ransomware changes the computer’s MBR so the normal boot process is interrupted and a ransom demand is displayed on screen instead.
- The Master Boot Record (MBR) is a section of the computer’s hard drive that allows the operating system to boot up.
- Example: Petya

Some details:
The modern ransomware use asymmetric encryption which requires both a public and private key. The public key is used to encrypt and verify data, while private key is used for decryption, each the inverse of the other.
The bad news is decryption is impossible unless a user has the private key stored on the cybercriminals’ server.
Some versions of known ransomware use symmetric encryption. This means one private key for all infected customers.
The good news is that several AV companies got the private keys by capturing the servers used by the ransomware CoinVault and Bitcryptor.
They are giving decryption programs for free.
How do they spread?
- In order to attack, Ransomware has to
–reach victim’s computer
- This is done normally via Email
–must be executed
- Normally by double clicking on a document, file, script.
- Uses some vulnerabilities of the system/software
Let’s have a look into details


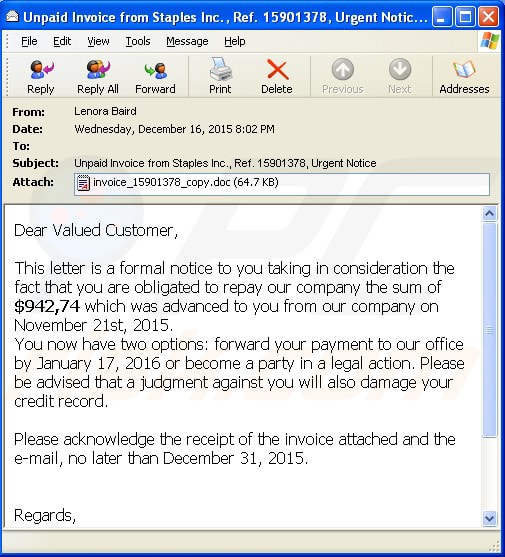
What is happening once you open ?
- The Java Script documents: download an EXE file and start it silently. After that the “standard” notification comes
- The Office documents: they contain macros in VB. They have a flag called “autostart” set which starts the macro by default. This macro downloads the payload and starts it from the current document.
- If the Macros are completely deactivated, or if macros are configured to not start automatically, then the cybercriminals are kindly asking the victim to enable it (see next slide)
- Angler exploit kit: exploits Adobe Flash (CVE-2015-0311) and, once successfully exploited, it downloads TeslaCrypt as a payload.
You get instructions to activate macros if they are not active by default:

They are expensive
The ransomware requests between 0.5 – 3 Bitcoins (100$-1500$).
What can we do against them?
First of all: create awareness so that users don’t infect themselves
- Train users, especially in companies, to deal with these threats
- No operating system is safe ! Yes, including MacOS and Android!
- Test everything, including the results of the training
- Teach administrators to configure the network properly:
–Network segmentation
–Proper user rights configured
–Use antimalware tools
–Backup often
–Deal with Macros – deactivate them entirely (via policies)!
–Deactivate execution of files from special folders (via policies)
–Activate User Access Control (UAC) (again)
- Second, automatic detection protection
- The malware authors release immediately a new version if they suspect that AV vendors added detection
- Detection Protection: cybercriminals test their malware against many scanners to make sure that their files are not detected. We need to have a way of avoiding this.
- Signature-based detection is failing here
- Signature detection helps usually maximum one day (but in general just few hours)
- The only automatic solution is to add
–generic detection for macros
–generic detection for macros with the AutoStart flag set
–Detection for code obfuscation in Javascript
–generic detection for archives with just one java script file inside
–URL filtering (generic or not)
- Solutions:
– Cloud based detection: this is complicated to achieve when we talk about Office Documents because of privacy reasons
– Heuristic and Generic Detection: ability to detect samples based on their format and on their actions, instead on their fingerprint
Tips to protect yourself
- Backup regularly
In case of infection you can get the latest version from the backup
- Don’t work with super admin rights
Most of the time, you don’t need to install of change things on your computer. A regular user is more than enough.
- Do not enable macros in Office
No comments. See the above picture 🙂
- Segment network
Not everybody needs access everywhere. Create network areas in such a way that people get access to only what they need.
- Patch software, hardware and operating system
Many ransomware versions exploit vulnerabilities in common software like Adobe Reader, Flash, Java. Keep only the software you need and keep it up to date. Do the same with the firmware of the devices like printers, scanners, etc.
Let your operating system update itself!
Last, but not least:
- Do not open just any attachment you receive
What to do if you clicked
There is, unfortunately, not much you can do. Just reduce and restrict damage.
If you clicked, shutdown your computer immediately by removing the power cord. If you shutdown from the button or using the operating system’s command, it will trigger a slow and safe shutdown process. This might be sometimes not enough.
After that, boot in safe mode without networking and run a full system scan. Chances are that the malware didn’t encrypt all your files if you were fast. Let the antivirus do its job and clean up the malware. Only after that boot the system normally.
If you have a backup then restore the files from there.
Think about Dropbox and alike. They keep several versions of the files and even if the malware encrypted the latest version and Dropbox synchronized it already, you can still revert to last known good version.
Safe safe!
